The
State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics named after K.E. Tsiolkovsky is the largest science museum in Russia and was established with the personal assistance of
Sergei Korolev and
Juri Gagarin, in 1967. In 1979, it was given a status of the scientific research institution, and in 1993 it was enlisted among the cultural and educational institutions of special social significance.
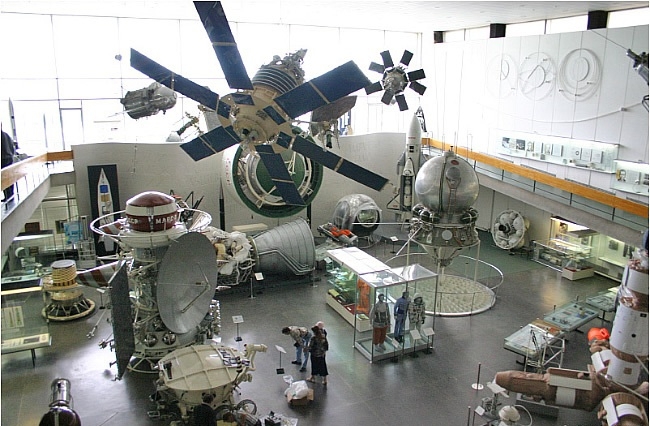

Spacecraft and space equipment form the bulk of the museum collection.
Photo credit: State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics
As a scientific research and technical center, this museum of cosmonautics coordinates the work of similar museums all over the country. Today its expositions reveal the history of aeronautics, aviation, and rocket-space engineering. Museum collection exhaustively represents the scientific heritage of K.E. Tsiolkovsky, one of the founders of theoretical cosmonautics, eminent inventor as well as the author of many works on philosophy and sociology.
Embracing the
Planetarium, the
Tsiolkovsky House Museum, the
Tsiolkovsky Apartment Museum, and the
Chizhevsky House Museum, the State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics occupies the total space of 5,374sqm and a new, bigger building (12,500sqm) is currently under construction.

Development of a new interactive exhibition area for children.
Photo credit: State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics
Each year the museum attracts 259,000 visitors by exhibiting 50,606 collection items, which are only 3.7% of its total collection. The plan is to build additional facilities to hold the rest and provide new space-related and entertaining programs. By 2020 the Museum will:
- connect all the facilities within the museum complex by means of the transportation network
- restore the original interior of the Tsiolkovsky and the Chizhevsky House Museums
- exhibit more pieces of real spacecraft and other space equipment
- use multimedia technologies to make exhibitions more interactive
- adopt active exhibition design, i.e. light, sound, VR
- introduce new space and flight simulators, especially for children
- give lectures on the connection between philosophy, history and space exploration
- share information on how to become an astronaut, or space engineer, to inspire youngsters
- build an open-air exhibition area with rockets and spaceships
- decorate the park surrounding the museum with space-related objects
- develop tourist itineraries and quests
- build a children's playground on the park territory.
The development of the State Museum of the history of cosmonautics is closely connected with the establishment of the city, Kaluga, to make the Russian museum known and acclaimed at the international level.
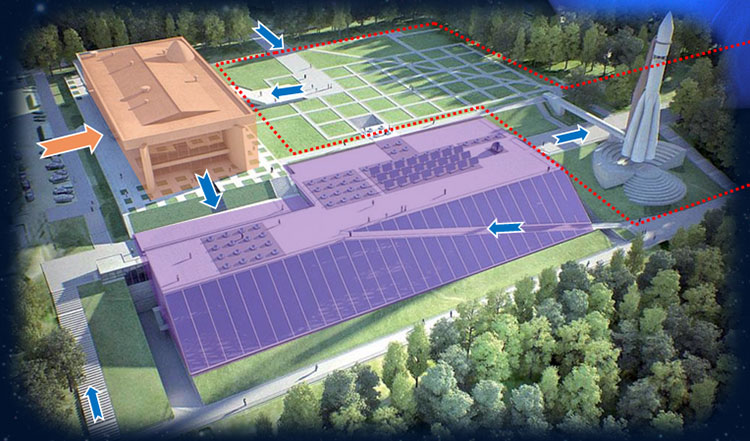
Plan of a new museum complex, including the main building, additional center, and open-air exhibition area.
Photo credit: State Museum of the History of Cosmonautics








